The ongoing growth of a major Indian city has helped experts to create a new way of understanding how urban sprawl happens, providing potential to improve people's lives across the Global South through better urban planning
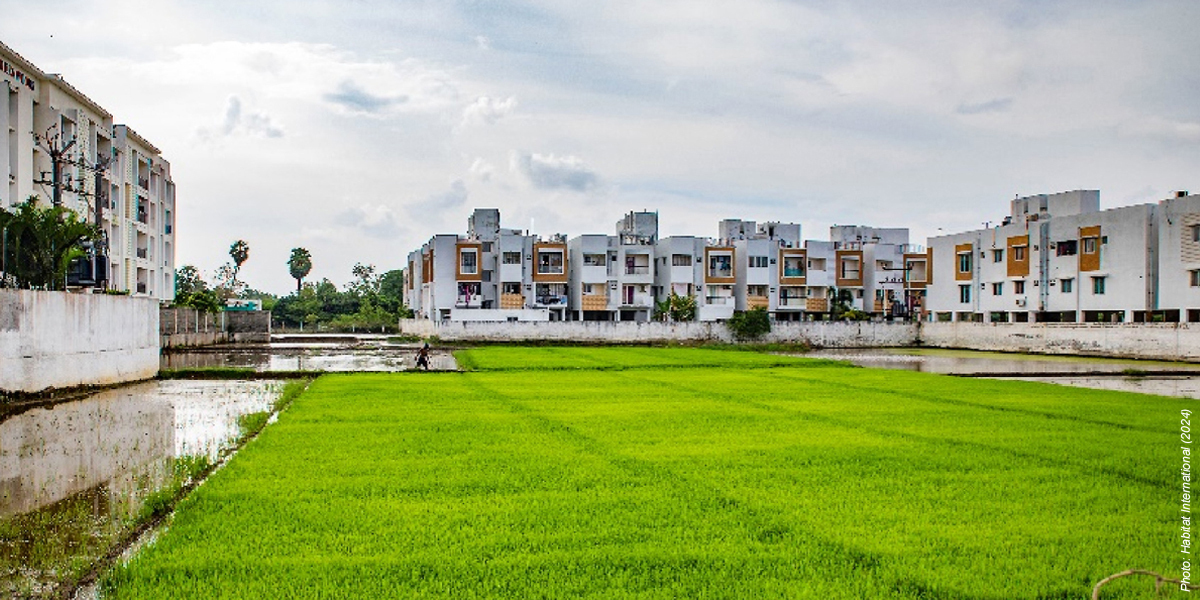

Researchers from the University of Birmingham in the UK analyzed the development of communities on the edge of Chennai, in South India, where urban and rural areas meet—known as the "peri-urban"—to develop an approach that is tailored to the needs of India and other countries in the Global South.
Despite a trend towards urbanization, 69% of India's population is still classified as rural. While Western planning efforts have been directed towards maintaining a distinct urban-rural divide, up to 140 million people live in India's "gray zone" settlements, which display both urban and rural characteristics.
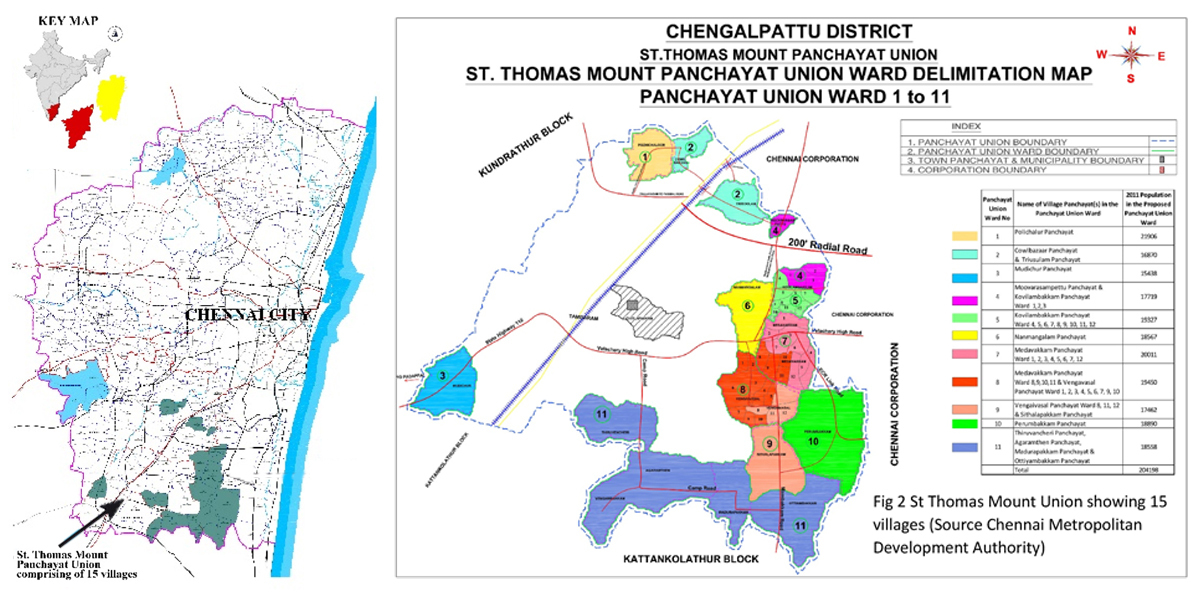
The research team published its findings in Habitat International after examining the rise of peri-urban regions within St. Thomas Mount Panchayat Union—15 villages on the fringes of Chennai.
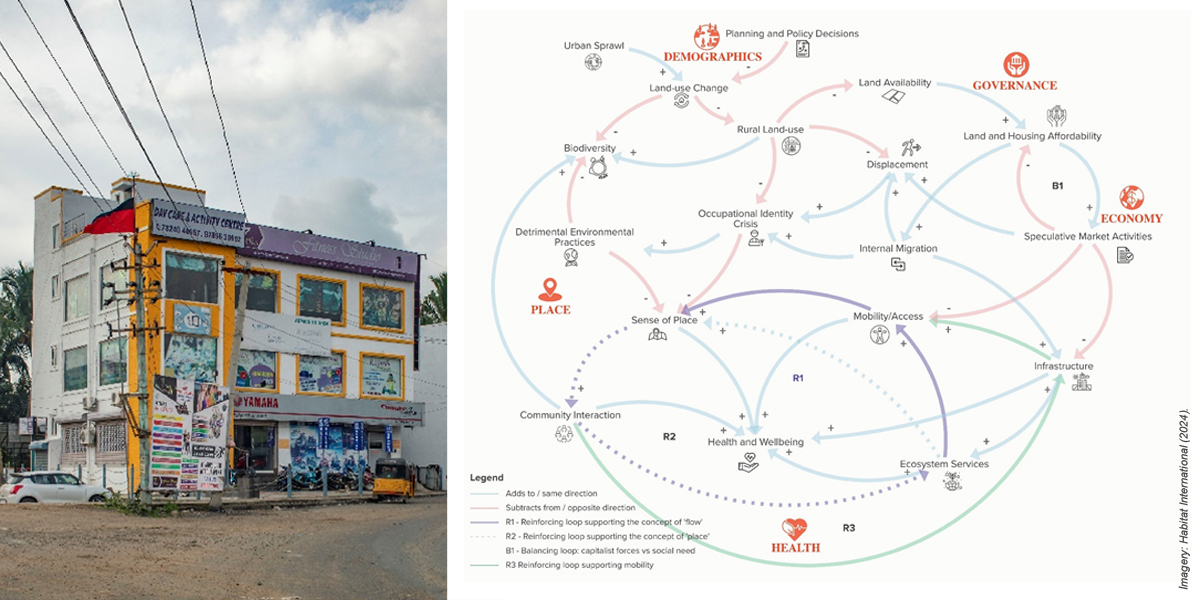
The researchers have developed a process that redefines the dynamics of such areas as the peri-urban turn using Causal Loop Diagrams to map the connections between health, place, demographics, governance, and economy
They have identified a number of elements that make up the peri-urban turn, including:
• Speculative development—Government targets peri-urban regions for projects requiring large land acquisitions, such as sewage treatment and slum resettlement.
• Sense of place—Peri-urban areas are perceived more as a "place" with rich sensorial and lived experiences, with everyday strongly linked to sights, sounds and smells.
• Ecosystem services—Such regions are primarily recognized for unfavourable environmental conditions, as well as inadequate hygiene and sanitation provisions.
• Mobility/access—Access to amenities and services significantly influences the overall quality of life for people in peri-urban areas
• Urban-rural coexistence—Instead of viewing rural and urban areas as separate spaces, there is a need to perceive them as a continuum.
Co-author Rahib Akhtar, from the University of Birmingham, commented, "With the rapid pace of urbanization, urban sprawl has become a prevalent phenomenon in the global South. This has created peri-urban spaces where city meets country—offering interactions between social, economic, and environmental systems that give valuable insight into how we can create better and more sustainable futures for the people living in these communities.
"Peri-urbanization can provide a way of better understanding the dynamics between urban and rural areas in India and the wider Global South. By examining peri-urbanization, we can gain a contextual understanding of the socio-spatial processes that shape urban and rural futures."
Apart from a lack of clarity in urban-rural classification in India, there is also ambiguity around the transformation and development of urban and rural areas. Confusion exists around the definition of such areas with terms including "urban village," "desakota" (village-town), predominantly urban, semi-urban, and potential urban areas.
The ambiguity surrounding the demarcation of urban and rural areas, combined with the complexities of local governance structures, creates challenges in understanding trends and patterns in India, with implications for people's aspirations, opportunities, challenges, and the need to migrate.
More information: Lakshmi Priya Rajendran et al, The 'peri-urban turn': A systems thinking approach for a paradigm shift in reconceptualising urban-rural futures in the global South, Habitat International (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.habitatint.2024.103041
Provided by University of Birmingham
Subscribe to our newsletter
Stay updated on the latest technology, innovation product arrivals and exciting offers to your inbox.
Newsletter

